In an era where healthcare has become an essential aspect of our lives, home health care services have emerged as a crucial option for individuals seeking medical assistance within the comfort of their own homes. These services offer convenience, personalization, and an opportunity for patients to maintain their independence while receiving the care they need. However, it’s essential to understand that home health care benefits typically do not cover everything, leaving many patients and their families facing unexpected costs and challenges. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the various aspects of home health care benefits, their limitations, and strategies to navigate these limitations effectively.
Contents
Understanding Home Health Care Benefits

Home health care benefits are designed to provide medical services and support to individuals who require assistance but wish to stay in the comfort of their homes. These benefits can be accessed through private health insurance plans, government-funded programs like Medicare or Medicaid, or even out-of-pocket payments.
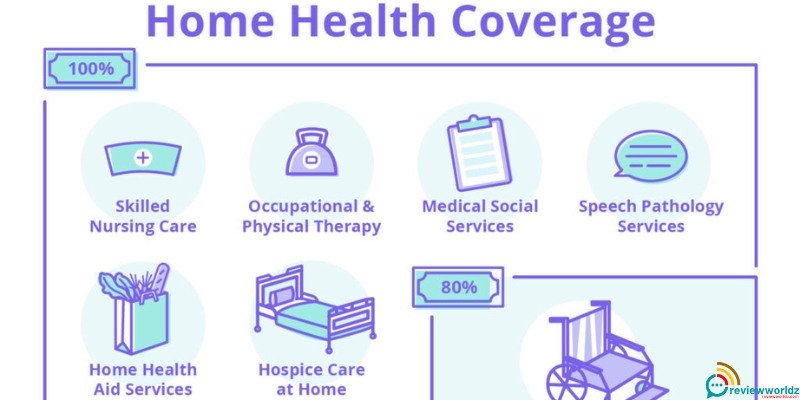
Common services covered by home health care benefits include:
1.1. Skilled Nursing Care: Registered nurses or licensed practical nurses can provide various medical services, such as administering medication, wound care, and monitoring vital signs.
1.2. Therapy Services: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can be offered to aid in rehabilitation and improving functional abilities.
1.3. Home Health Aides: Aides can assist with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and meal preparation.
1.4. Medical Social Services: Social workers can provide emotional support, connect patients with community resources, and help with end-of-life planning.
1.5. Home Health Equipment and Supplies: Some plans cover necessary medical equipment and supplies like wheelchairs, oxygen, or wound care supplies.
The Limitations of Home Health Care Benefits

Despite the numerous advantages of home health care, these benefits often come with limitations that can be challenging for patients and their families. Here are some of the common limitations:
2.1. Limited Hours and Visits: Most home health care benefits have restrictions on the number of hours and visits a patient can receive. These limitations may not adequately cover the needs of patients with chronic or complex conditions.
2.2. Eligibility Criteria: Eligibility for home health care benefits may depend on specific criteria, such as medical necessity, homebound status, or the need for skilled care. Not all individuals may meet these criteria.
2.3. Incomplete Coverage: Home health care benefits may not cover all necessary services. For instance, they might cover skilled nursing care and therapy but not personal care assistance or specialized equipment.
2.4. Copayments and Deductibles: Patients often need to pay copayments, deductibles, or coinsurance for home health care services, leading to unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
2.5. Service Availability: The availability of home health care services may be limited in certain geographic areas, which can make it challenging for patients in rural or remote locations to access care.
2.6. Changes in Health Status: Patients who no longer meet the eligibility criteria may lose their home health care benefits, even if their health deteriorates.
Why Home Health Care Benefits Typically Do Not Cover Everything

While home health care benefits have their limitations, there are several strategies patients and their families can employ to navigate these challenges effectively:
3.1. Thoroughly Review Insurance Policies: Understand the details of your insurance policy, including coverage limits, copayments, and eligibility criteria. This knowledge can help you make informed decisions about home health care services.
3.2. Advocate for Your Needs: If you believe that your current benefits are insufficient to meet your medical needs, don’t hesitate to advocate for additional services or seek a care plan review with your healthcare provider.
3.3. Explore Alternative Funding Sources: Investigate other potential funding sources, such as grants, community programs, or nonprofit organizations, that might help cover the costs of home health care.
3.4. Plan for the Future: For individuals with progressive conditions, it’s essential to plan for potential changes in care needs and explore options like hospice or long-term care facilities.
3.5. Seek Professional Advice: Consult with healthcare professionals or social workers who specialize in home health care to navigate the complexities of the system and identify available resources.
3.6. Utilize Family and Community Support: Enlist the help of family members, friends, and community support networks to supplement home health care services, particularly when limitations exist.
Conclusion
Home health care benefits undoubtedly provide a valuable and convenient option for individuals in need of medical assistance. However, it’s vital to acknowledge and understand the limitations that often accompany these benefits. By educating oneself, advocating for appropriate care, and exploring alternative funding sources, patients and their families can better navigate the complexities of home health care and ensure that their healthcare needs are met effectively, regardless of the limitations imposed by their benefits. Ultimately, the goal should be to strike a balance between the advantages of home health care and the need for comprehensive and affordable healthcare services.